what did rutherford's gold foil experiment help him conclude
Who did the Gold Thwart Experiment?
The gold foil experiment was a pathbreaking work conducted aside scientists Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden under the supervision of Alfred Bernhard Nobel laureate physicist Ernest Rutherford that led to the discovery of the appropriate bodily structure of an atom. Called the Geiger-Marsden experiment, it was performed at the Physical Laboratories of the University of Manchester between 1908 and 1913.
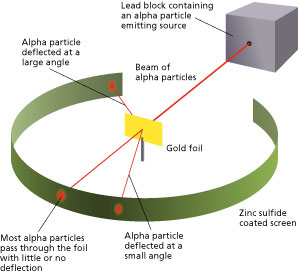
Gold Foil Experiment
History
The prevalent atomic theory at the time of the enquiry was the plum pudding model that was developed by Overlord Kelvin and further improved by J.J. Thomson. Reported to the theory, an atom was a positively charged sphere with the electrons embedded in it like plums in a Christmas pudding.
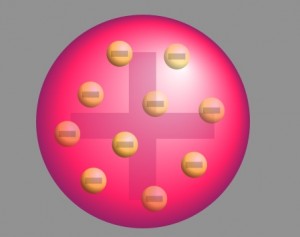
With neutrons and protons yet to equal disclosed, the theory was copied following the classical Newtonian Physics. However, in the absence of experimental proof, this approach lacked real acceptance by the scientific community.
What is the Gold Foil Experiment?
Verbal description
The method used by scientists enclosed the following research steps and subprogram. They bombarded a thin gold foil of thickness approximately 8.6 x 10-6 cm with a beam of alpha particles in a vacuum. Exploratory particles are positively hot particles with a mass of about quadruplet multiplication that of a hydrogen atom and are found in radioactive natural substances. They used gilded since it is highly malleable, producing sheets that can be only when a few atoms thick, thereby ensuring smooth passage of the alpha particles. A broadside screen backed with Zn sulphide surrounded the foil. Since the charged alpha particles possess mass and move very andantino, it was hypothesized that they would penetrate the thin gold foil and land themselves along the screen, producing fluorescence in the part they struck.
Like the Christmas pudding model, since the positive charge of atoms was equally distributed and as well small as compared thereto of the alpha particles, the deflection of the particulate was foreseen to be less than a small fraction of a degree.
Observation
Though near of the important particles behaved As expected, on that point was a noticeable divide of particles that got scattered by angles greater than 90 degrees. On that point were about 1 in every 2000 particles that got scattered by a full 180 academic degree, i.e., they retraced their path after hitting the chromatic foil.
Simulation of Ernest Rutherford's Metallic Foil Experiment
Courtesy: University of Colorado River Boulder
Conclusion
The unexpected outcome could have only one account – a highly concentrated positive burster at the center of an atom that caused an static repulsion of the particles strong enough to bounce them back down to their source. The particles that got deflected by huge angles passed approximately the said concentrated mass. Most of the particles moved undeviated as thither was no obstruction to their path, proving that the bulk of an atom is empty.
In addition to the above, First Baron Rutherford of Nelson ended that since the central core could deflect the dense alpha particles, information technology shows that almost the intact mass of the atom is massed thither. Rutherford titled it the "nucleus" after experimenting with various gases. He also utilized materials different than gold for the foil, though the gold thwart version gained the most popularity.
He farther went on to reject the plum tree pudding model and developed a new atomic structure called the planetary model. In that model, a immensely empty atom holds a lilliputian nucleus at the kernel enclosed by a cloud of electrons. As a result of his gold foil experiment, Rutherford's atomic theory holds redemptive even now.
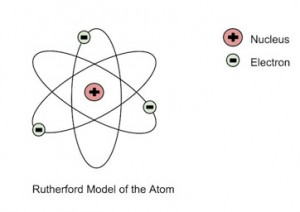
Rutherford's Atomic Model
Rutherford's Gold Double cross Experiment Vitality
Summary
- Rutherford demonstrated his experiment happening bombarding thin gold thwart with alpha particles contributed immensely to the atomic theory by proposing his nuclear atomic model.
- The nuclear model of the mote consists of a small and dense positively positively charged interior surrounded by a cloud of electrons.
- The significance and purpose of the gold foil experiment are still prevalent now. The discovery of the core group paved the way for further research, unraveling a list of nameless basic particles.
-
References
Article was survive reviewed on Wednesday, September 8, 2021
what did rutherford's gold foil experiment help him conclude
Source: https://www.sciencefacts.net/gold-foil-experiment.html
Posting Komentar untuk "what did rutherford's gold foil experiment help him conclude"